Introduction
Hey there! Have you ever wondered what makes Bitcoin and Ethereum different? These two are like the superheroes of the cryptocurrency world, but they have their own special powers.
Bitcoin was created in 2009 by someone (or a group) using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. Think of it like digital gold. On the other hand, a young genius named Vitalik Buterin introduced Ethereum in 2015. It’s like a giant app store where people can build their own programs.
People use Bitcoin mainly as a way to store value and make payments. It’s like using digital money. Ethereum is different. For example, artists can create their own digital art and sell it using Ethereum, thanks to those smart contracts.
Bitcoin sometimes faces slow transaction times, like waiting in a long line at a busy store. Ethereum, on the other hand, is working on upgrades to handle more transactions quickly, like opening new checkout lanes.
Bitcoin has a strong community focused on keeping it secure and stable while Ethereum’s community is like a bunch of tech enthusiasts who love experimenting and building new things.
So, while Bitcoin and Ethereum are both important in the world of digital finance, they serve different purposes. Bitcoin is great for transactions and saving value, while Ethereum is perfect for creating and running apps. Isn’t it cool how these two digital giants work? Understanding their differences helps us see how each contributes uniquely to the digital world
Differences Between Bitcoin and Ethereum
The main differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum are:
1. Origins and Purpose
Bitcoin
Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2008 and launched the network in 2009. Think of Bitcoin as digital gold. Its main goal is to be a decentralized digital currency, which means you can send money directly to someone else without needing a bank. This makes it a great way to store value and protect against inflation.
Ethereum
Ethereum was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 and launched in 2015. Unlike Bitcoin, which is like digital money, Ethereum is like a giant app store. It allows developers to create smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps). Smart contracts are like digital agreements that automatically execute when certain conditions are met, making transactions smooth and trustless.
2. Technology and Architecture
Bitcoin
Bitcoin works using blockchain technology, where each block contains a bunch of transactions. Firstly, the network stays secure thanks to a system called Proof-of-Work (PoW). In this system, miners solve tough math problems to confirm transactions and keep everything safe. For instance, imagine a huge puzzle that needs to be solved to add new transactions. This process, in turn, uses a lot of computing power, which ultimately ensures the network remains strong and secure.
Ethereum
Ethereum also uses blockchain technology but takes it a step further with something called the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The EVM allows smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps) to run on the Ethereum network. While it started with Proof-of-Work like Bitcoin, Ethereum is moving to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with Ethereum 2.0. Instead of solving puzzles, validators propose and check blocks based on the coins they own and stake. This change aims to make Ethereum faster and more energy-efficient.
For example, a game on Ethereum could automatically reward players with digital tokens based on their achievements without needing a central authority to manage it.
3. Use Cases
Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s main job is to be digital money and a way to store value. You can send and receive Bitcoin directly to anyone around the world without needing a bank. It’s like sending an email but with money. However, Bitcoin is kept simple on purpose, so it mostly handles basic transactions.
Ethereum
Ethereum is like a giant playground for developers to build smart contracts and apps called dApps. This flexibility means it can be used for all sorts of things, like DeFi apps for loans and trading, digital art called NFTs, and even voting systems. For example, a smart contract on Ethereum could automatically transfer ownership of a digital art piece once it’s paid for, without needing a middleman.
4. Supply and Scalability
Bitcoin
Bitcoin has a limit of 21 million coins, which makes it rare like digital gold. This scarcity helps increase its value. But, Bitcoin can be slow; each transaction block takes about 10 minutes to process. When lots of people use Bitcoin, it can get even slower and more expensive to send transactions.
Ethereum
Ethereum doesn’t have a fixed number of coins. At first, new Ether (ETH) was created through mining, but now with Ethereum 2.0, it’s created through staking. This change should slow down how fast new ETH is made. Ethereum is faster than Bitcoin, processing transactions in about 15 seconds. Though it faces some speed and cost issues, Ethereum is working on solutions like sharding and layer 2 technologies to make transactions quicker and cheaper. For example, sharding will split the network into smaller pieces to process transactions faster.
5. Community and Development
Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s developers focus heavily on keeping it secure and stable. They make updates very carefully to ensure it remain reliable. This cautious approach helps Bitcoin stay known as a safe and stable way to store value. Additionally, they prioritize security above all else, which means changes are slow but steady. For example, they might wait months to introduce a new feature just to make sure it’s perfect. As a result, Bitcoin has earned a reputation as one of the most trusted digital currencies out there.
Ethereum
Ethereum has a lively and creative development community that loves innovation and frequent updates. They constantly come up with new ideas. For example, the ongoing Ethereum 2.0 upgrade aims to make the network faster, safer, and more sustainable. This shows how Ethereum is always looking to improve and expand what it can do.
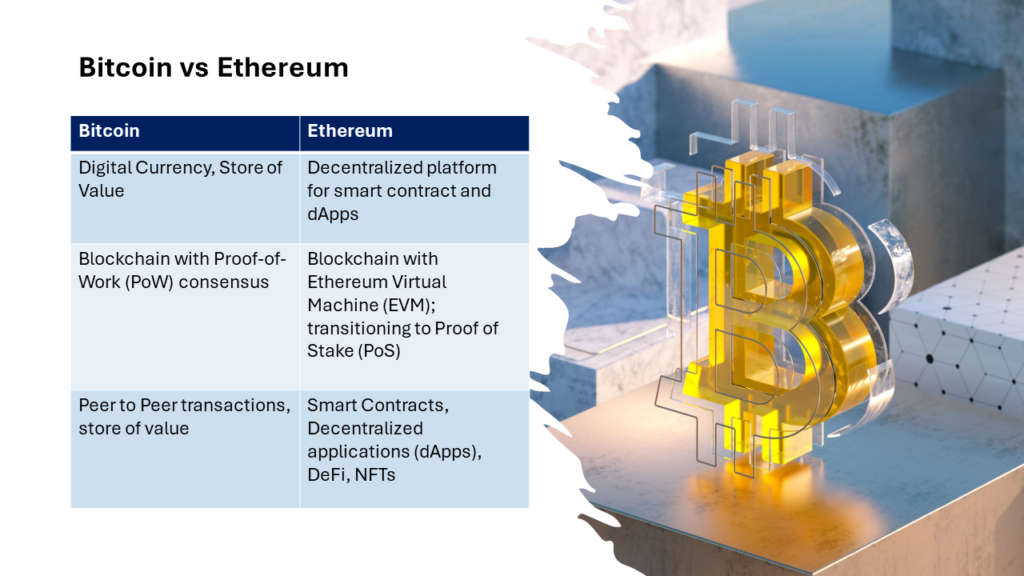
Table summarizing the differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum
| Aspect | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
| Creation | Created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009 | Proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2013, launched in 2015 |
| Primary Purpose | Digital currency and store of value | Decentralized platform for smart contracts and dApps |
| Technology | Blockchain with Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus | Blockchain with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM); transitioning to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
| Use Cases | Peer-to-peer transactions, store of value | Smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi, NFTs |
| Supply Limit | Capped at 21 million coins | No fixed supply; inflationary model initially, with decreasing issuance in Ethereum 2.0 |
| Transaction Speed | Average block time of ~10 minutes | Average block time of ~15 seconds |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; higher fees and slower transactions during high demand | Ongoing scalability improvements (e.g., sharding, layer 2 solutions) |
| Development Focus | Stability and security; conservative updates | Innovation and rapid updates; active development community |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Initially Proof-of-Work (PoW); transitioning to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
| Script Capability | Limited scripting for security and simplicity | Extensive scripting for complex applications via smart contracts |
Conclusion
So, in a nutshell, while both Bitcoin and Ethereum are major cryptocurrencies, they do different things. Bitcoin is mainly digital money and a way to store value, with a fixed supply and a strong focus on security. Ethereum, however, is a flexible platform where you can create smart contracts and decentralized apps. It’s always evolving to become faster and more useful. Understanding these differences helps us see how each one uniquely contributes to the world of digital finance. Check Crypto Evolution 2025
FAQ of BitCoin, Click Here

